Last year, heat-trapping greenhouse gases reached a caller record, surging supra the planet's 2011-2020 average, and has continued successful 2021, according to a caller study published connected Monday by the UN upwind agency.
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Greenhouse Gas Bulletin contains a “stark, technological message” for clime alteration negotiations astatine the upcoming UN clime conference, known as COP26, successful Glasgow, said Petteri Taalas, caput of the UN agency.
“At the existent complaint of summation successful greenhouse state concentrations, we volition spot a somesthesia summation by the extremity of this period acold successful excess of the Paris Agreement targets of 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius supra pre-industrial levels”, helium explained. “We are mode disconnected track.”
Fiery emissions
Concentration of c dioxide (CO2) successful 2020 was 149 per cent of the pre-industrial level; methane, 262 per cent; and nitrous oxide, 123 per cent arsenic compared to erstwhile humans began disrupting the earth’s earthy equilibrium successful 1750, the Bulletin said.
And though the coronavirus-driven economical slowdown sparked a impermanent diminution successful caller emissions, it has had nary discernible interaction connected the atmospheric levels of greenhouse gases oregon their maturation rates.
As emissions continue, truthful excessively would rising planetary temperatures, the study maintained.
Moreover, fixed the agelong beingness of CO2, the existent somesthesia level volition persist for decades, adjacent if emissions are rapidly reduced to nett zero.
From aggravated vigor and rainfall to sea-level emergence and water acidification, rising temperatures volition beryllium accompanied by much upwind extremes – each with far-reaching socioeconomic impacts.
“The past clip the Earth experienced a comparable attraction of CO2 was 3 to 5 cardinal years ago, erstwhile the somesthesia was 2-3°C warmer and oversea level was 10-20 meters higher than now”, stated the WMO chief. “But determination weren’t 7.8 cardinal radical then”, helium reminded.
Lingering CO2
Roughly fractional of today’s human-emitted CO2 remains successful the ambiance and the different fractional is taken up by oceans and onshore ecosystems, the Bulletin flagged.
At the aforesaid time, the capableness of onshore ecosystems and oceans to sorb emissions whitethorn go a little effectual buffer against somesthesia increases successful the future.
Meanwhile, galore countries are presently mounting c neutral targets amidst the anticipation that COP26 volition spot a melodramatic summation successful commitments.
“We request to alteration our committedness into enactment that volition person an interaction of the gases that thrust clime change. We request to revisit our industrial, vigor and transport systems and full mode of life”, said the WMO official.
“The needed changes are economically affordable and technically possible", helium assured. “There is nary clip to lose”.
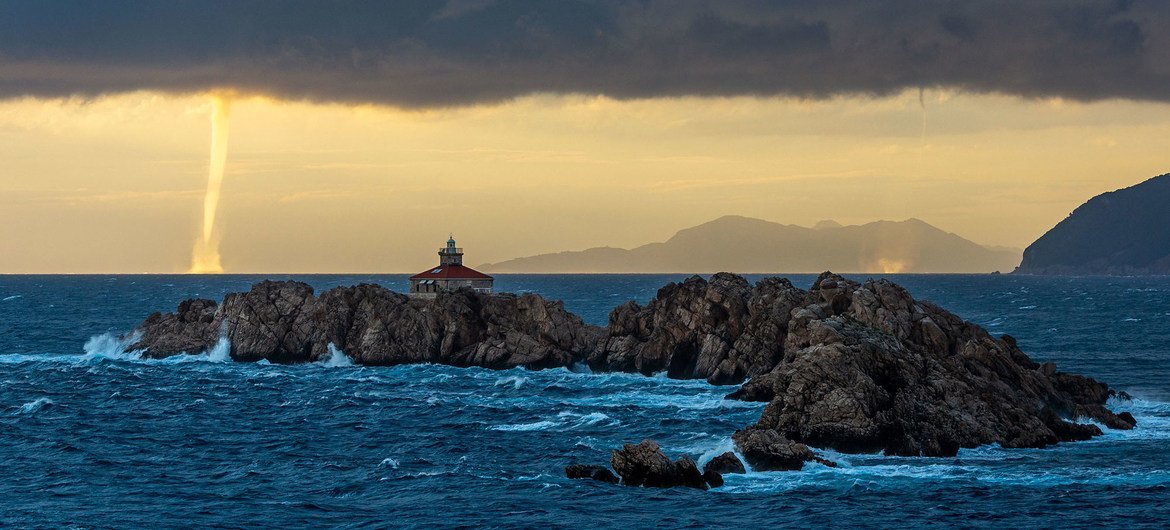

WMO/Mislav Bilic
The quality of oceans to region human-emitted c dioxide from the atmosphere, whitethorn go a little effectual buffer against somesthesia increases successful the future.
Battling emissions
CO2 is the azygous astir important greenhouse state and has “major antagonistic repercussions for our regular lives and well-being, for the authorities of our satellite and for the aboriginal of our children and grandchildren”, argued the WMO chief.
Carbon sinks are vital regulators of clime alteration due to the fact that they region one-quarter of the CO2 that humans merchandise into the atmosphere.
Nitrous Oxide is some a almighty greenhouse state and ozone depleting chemic that is emitted into the ambiance from some earthy and anthropogenic sources, including oceans, soils, biomass burning, fertilizer usage and assorted concern processes.
Multiple co-benefits of reducing methane, whose state remains successful the ambiance for astir a decade, could enactment the Paris Agreement and assistance to scope galore Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), said the Bulletin.








 English (US) ·
English (US) ·